Raspberry Pi Resource Monitor SSH: Your Ultimate Guide To Streamlining Remote Management
Ever wondered how you can keep tabs on your Raspberry Pi's performance without being physically present? Well, buckle up because today we're diving deep into the world of Raspberry Pi resource monitoring via SSH. If you're a tech enthusiast, hobbyist, or even a professional, this guide is your golden ticket to mastering remote management like a pro.
Let’s face it – Raspberry Pi has become the go-to device for countless projects, from home automation to weather stations. But here’s the kicker: when you’re managing multiple Pis or need to troubleshoot issues remotely, having a reliable resource monitor over SSH can save your bacon. In this article, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know, from setting up SSH to monitoring CPU, memory, and disk usage like a boss.
Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced user, this guide will equip you with the tools and knowledge to take your Raspberry Pi management game to the next level. So, grab a cup of coffee, sit back, and let’s get started!
- Embracing The Journey Growing Out Short Hair Over 50
- Funky Hairdos The Ultimate Guide To Unleashing Your Inner Rock Star
Table of Contents
- What is SSH and Why It Matters for Raspberry Pi?
- Setting Up SSH on Your Raspberry Pi
- Understanding Raspberry Pi Resource Monitoring
- Top Tools for Raspberry Pi Resource Monitoring via SSH
- Using the 'top' Command for Real-Time Monitoring
- Monitoring CPU Usage via SSH
- Tracking Memory Usage on Raspberry Pi
- Checking Disk Space and Storage
- Tips for Optimizing Raspberry Pi Performance
- Common Issues and How to Troubleshoot
What is SSH and Why It Matters for Raspberry Pi?
First things first, let’s break down what SSH really is. SSH, or Secure Shell, is a cryptographic network protocol that allows you to securely connect to remote devices over an unsecured network. Think of it as a secure tunnel that lets you access your Raspberry Pi from anywhere in the world. For Raspberry Pi enthusiasts, SSH is a game-changer because it eliminates the need for a monitor, keyboard, or mouse – all you need is a laptop or smartphone.
Here’s the deal: when you’re running resource-intensive applications or managing multiple Pis, being able to monitor and manage them remotely is crucial. SSH not only provides secure access but also allows you to run commands, transfer files, and monitor system resources with ease.
So, why does SSH matter for Raspberry Pi? Simple – it gives you the flexibility to manage your device from anywhere, whether you’re at home, at work, or sipping coffee at a café. Plus, it’s free, easy to set up, and super reliable. Now, let’s move on to the next step – setting it up!
- 2024 Womens Hair The Ultimate Guide To Trendsetting Styles
- Hairstyles For Round Faces Over 50 Finding Your Perfect Look
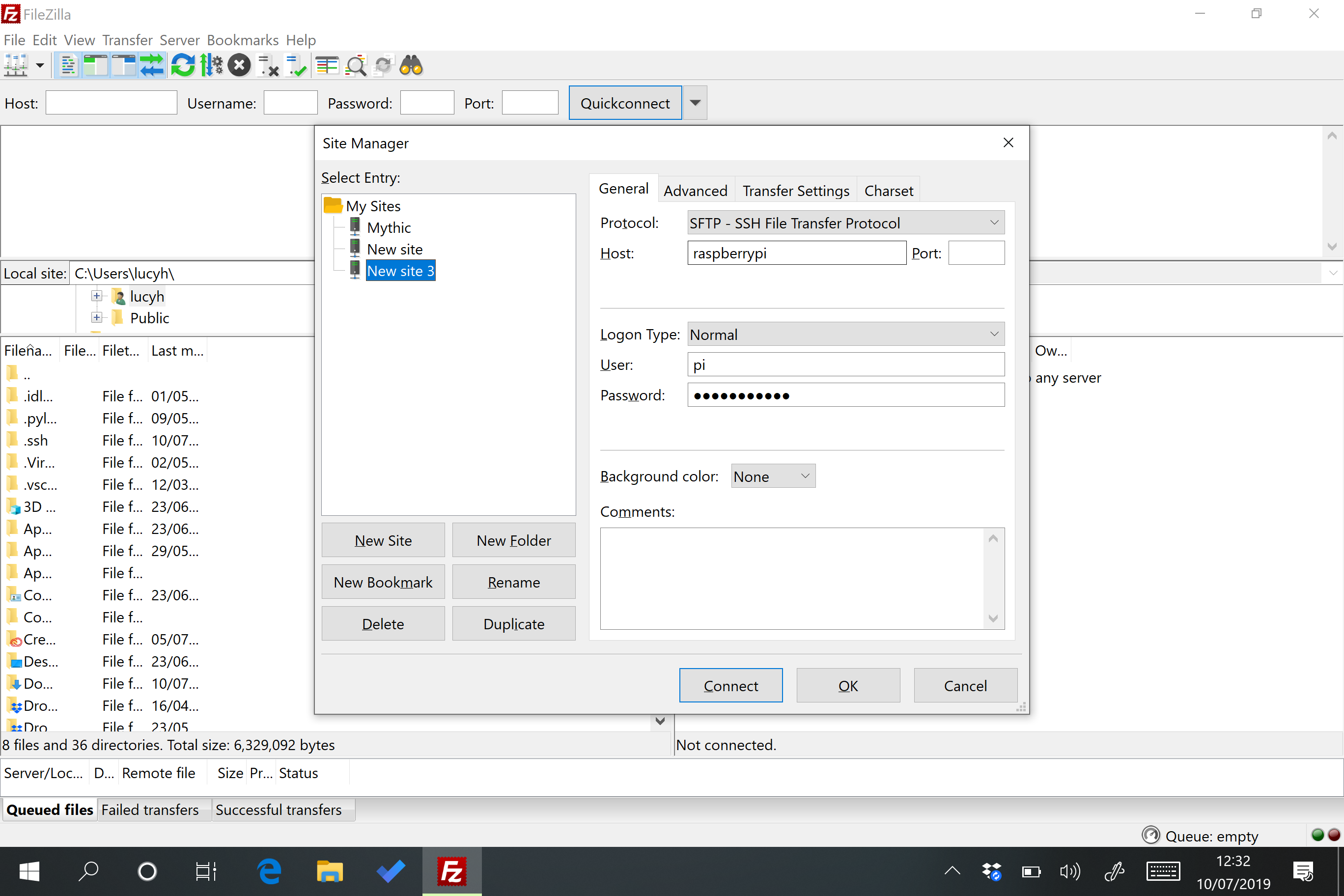
Setting Up SSH on Your Raspberry Pi
Setting up SSH on your Raspberry Pi is a breeze, even if you’re a newbie. Here’s a quick rundown of how to do it:
Step 1: Enable SSH on Your Raspberry Pi
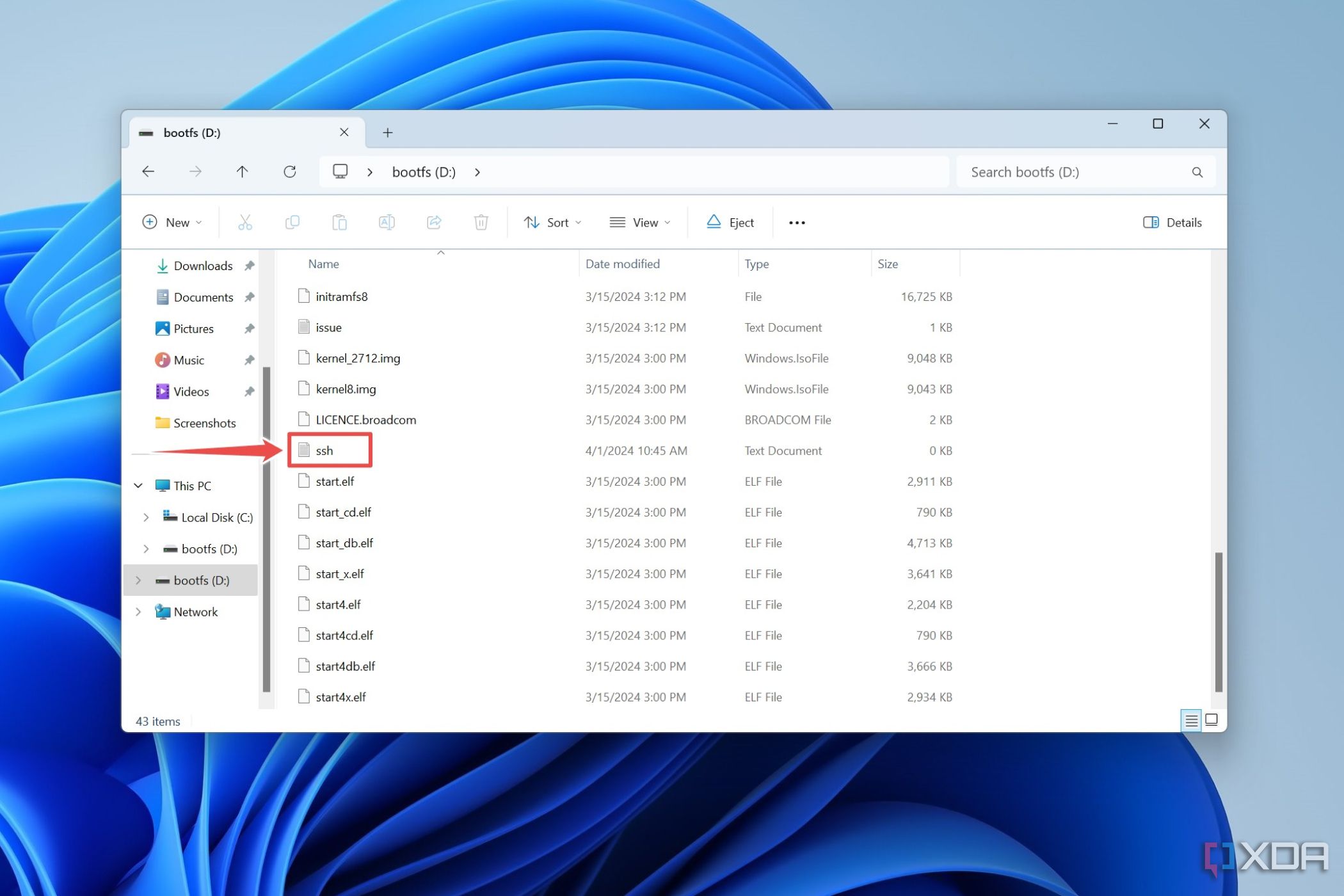
By default, SSH is disabled on newer versions of Raspberry Pi OS. To enable it, follow these steps:
- Boot up your Raspberry Pi and log in.
- Open the terminal and type
sudo raspi-config. - Navigate to
Interfacing Optionsand selectSSH. - Choose
Enableand hitOK.
That’s it! SSH is now enabled on your Raspberry Pi. If you’re using a headless setup (no monitor), simply create an empty file named ssh in the boot partition of your SD card before powering on your Pi.
Step 2: Connect to Your Raspberry Pi via SSH
Now that SSH is enabled, it’s time to connect to your Pi from another device. Here’s how:
- Find your Raspberry Pi’s IP address by typing
hostname -Iin the terminal. - On your laptop or smartphone, use an SSH client like PuTTY (Windows) or Terminal (Mac/Linux).
- Enter the Pi’s IP address and log in using your credentials (default username is
piand password israspberry).
Voilà! You’re now connected to your Raspberry Pi via SSH and ready to start monitoring resources.
Understanding Raspberry Pi Resource Monitoring
Resource monitoring is all about keeping an eye on your Raspberry Pi’s performance. Whether you’re running a web server, hosting a media center, or building a smart home system, knowing how your Pi is performing is key to ensuring smooth operation. With SSH, you can monitor CPU usage, memory consumption, disk space, and more – all from the comfort of your couch.
Here’s why resource monitoring matters:
- Prevent Overloads: By monitoring CPU and memory usage, you can identify potential bottlenecks before they cause issues.
- Optimize Performance: Knowing which processes are consuming the most resources allows you to fine-tune your setup for better performance.
- Ensure Stability: Regular monitoring helps you catch errors or crashes early, keeping your projects running smoothly.
In the next section, we’ll explore some of the best tools for Raspberry Pi resource monitoring via SSH.
Top Tools for Raspberry Pi Resource Monitoring via SSH
When it comes to monitoring resources on your Raspberry Pi, there’s no shortage of tools to choose from. Here are some of the best ones:
1. htop
htop is a powerful interactive process viewer that provides a real-time overview of your Pi’s CPU, memory, and disk usage. It’s easy to use and offers a colorful, intuitive interface. To install htop, simply type sudo apt install htop in the terminal.
2. Glances
Glances is another excellent tool for monitoring system resources. It supports multiple outputs, including SSH, and offers detailed insights into CPU, memory, disk, and network usage. Install it with sudo apt install glances.
3. vmstat
For those who prefer lightweight solutions, vmstat is a great choice. It provides a snapshot of your Pi’s CPU, memory, and disk activity. Use vmstat 1 to get real-time updates every second.
These tools, combined with SSH, give you unparalleled control over your Raspberry Pi’s performance. Let’s dive deeper into how you can use them effectively.
Using the 'top' Command for Real-Time Monitoring
If you’re looking for a quick and easy way to monitor your Raspberry Pi’s resources, the top command is your best friend. It provides a real-time view of system processes, CPU usage, memory consumption, and more. Here’s how to use it:
- Type
topin the terminal to open the interface. - Use the arrow keys to navigate and sort processes by CPU or memory usage.
- Press
qto exit the interface.
The top command is perfect for identifying resource-hungry processes and troubleshooting performance issues. For more advanced users, consider upgrading to htop for a more feature-rich experience.
Monitoring CPU Usage via SSH
Monitoring CPU usage is crucial, especially if you’re running heavy applications or multiple processes on your Raspberry Pi. Here’s how you can do it:
Method 1: Using the 'top' Command
As we discussed earlier, the top command provides a real-time view of CPU usage. Look for the %CPU column to see which processes are consuming the most resources.
Method 2: Using 'mpstat'
For more detailed CPU statistics, use the mpstat command. Install it with sudo apt install sysstat and run mpstat to get a breakdown of CPU usage by core.
By keeping an eye on CPU usage, you can ensure your Raspberry Pi is running at optimal levels and avoid overheating or crashes.
Tracking Memory Usage on Raspberry Pi
Memory is another critical resource to monitor, especially if you’re running memory-intensive applications. Here’s how you can track memory usage:
Method 1: Using the 'free' Command
The free command provides a quick overview of your Pi’s memory usage. Simply type free -h to see the total, used, and available memory in a human-readable format.
Method 2: Using 'vmstat'
For more detailed memory statistics, use the vmstat command. Run vmstat 1 to get real-time updates every second.
By monitoring memory usage, you can identify memory leaks, optimize your applications, and ensure your Pi runs smoothly.
Checking Disk Space and Storage
Running out of disk space can bring your Raspberry Pi projects to a screeching halt. That’s why it’s important to regularly check your storage usage. Here’s how:
Method 1: Using the 'df' Command
The df command shows the disk space usage on your Pi. Type df -h to get a human-readable overview of your storage.
Method 2: Using 'du'
To find out which files and directories are taking up the most space, use the du command. Run du -sh * to see the size of each file and folder in the current directory.
By keeping an eye on disk space, you can free up storage, prevent crashes, and ensure your projects run seamlessly.
Tips for Optimizing Raspberry Pi Performance
Now that you know how to monitor your Raspberry Pi’s resources, here are some tips to optimize its performance:
- Upgrade Your SD Card: Use a high-speed SD card to improve read/write speeds.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Stop services you don’t use to free up resources.
- Update Your Software: Keep your Pi’s software up to date for better performance and security.
- Use Lightweight Applications: Opt for lightweight alternatives to heavy software.
By following these tips, you can squeeze every bit of performance out of your Raspberry Pi and ensure it runs like a well-oiled machine.
Common Issues and How to Troubleshoot
Even with the best monitoring tools, issues can still arise. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them:
Issue 1: High CPU Usage
If your CPU usage is consistently high, try identifying the culprit using the top command. Once you’ve pinpointed the problematic process, consider stopping or optimizing it.
Issue 2: Low Memory
Running out of memory? Use the free command to check your memory usage and clear up unnecessary processes. You can also add a swap file to increase available memory.
Issue 3: Disk Space Full
If your disk space is full, use the df and du commands to identify large files and folders. Delete unnecessary files or move them to an external drive to free up space.
With these troubleshooting tips, you’ll be able to tackle most issues that come your way and keep your Raspberry Pi running smoothly.
Conclusion
And there you have it – your ultimate guide to Raspberry Pi resource monitoring via SSH. From setting up SSH to using powerful tools like htop and Glances, you now have the knowledge and tools to manage your Raspberry Pi like a pro. Remember, monitoring your Pi
- Over 60 Medium Length Hairstyles Timeless Elegance For Every Woman
- Unveiling The World Of Movierulz Rx 100 Your Ultimate Movie Streaming Guide
SSH Remote control your Raspberry Pi — Raspberry Pi Official Magazine

Raspberry Pi How to enable SSH
How to SSH into Raspberry Pi for Remote Access on Windows